Periodontal Disease Can Cause Oral Health Issues
Sleep Apnea is a Serious Condition
June 3, 2014Treatment for Missing Teeth
June 17, 2014Periodontal disease is known to cause cause serious oral health issues, including swollen gums, bleeding gums, chronic bad breath, or very sensitive teeth. Periodontal disease may develop just about any time, in many stages. If we understand the root causes and cures, we can better align toward good oral health.
What Defines Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease is simply, disease of or to the gums, and a large many U.S. adults have the disease in some form. From simple inflammation to the gums, too much more serious disease conditions that can result in permanent tissue damage or even bone loss.
Periodontal disease is mainly caused by the presence of plaque, which happens when bacteria present in our mouths combine with mucous and create a transparent, sticky substance on our teeth. The main defense against this is regular brushing and flossing, as this assist in ridding your mouth of plaque. If plaque is not removed it hardens and forms tartar. Brushing alone will not remove tartar, so brushing regularly is your best defense, however, be sure to visit your dentist regularly to rid your mouth of the hardened tarter not removed by brushing.
What Are the Most Typical Periodontal Diseases?
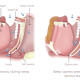
The two main periodontal diseases are Periodontis and Gingivitis. Gingivitis is caused by Bacteria in the mouth enflaming the gums. Indicators of Gingivitis are swollen, red gums that easily bleed frequently. This is a mild disease and can be corrected by flossing regularly, brushing often and of course, regular cleanings. This disease does not result in bone or tissue loss, so it is something you can get under control.
However, Gingivitis, if not treated, can develop into Periodontis. And Periodontis is much more serious. Gums move away from teeth and form pockets that often become infected, which in some cases, although rare, can result in life-threatening conditions. This is because the immune system fights the bacteria as the plaque continues to grow and spread below the gum line. This often results bone and tissue loss, which are needed to hold the teeth in position. Periodontis can lead to further issues, such as crooked teeth and more serious conditions if left untreated.
Is Periodontal Disease Easy to Treat?
With periodontal disease, the main goal is to get and keep the infection under control. Once that is accomplished, the diseased area must be evaluated to see the extent of the damage so a treatment plan can be recommended. Treatment typically can include:
- Administering Oral Medications
- Root planning and Scaling
- Surgical Procedures
Is Periodontal Disease Preventable?
The main way to prevent periodontal disease is to keep your mouth healthy, brush at least two times each day and floss often (daily if possible) to remove plaque that hides between teeth. Regular dental visits can ensure if the disease forms, quick treatment can be applied.
